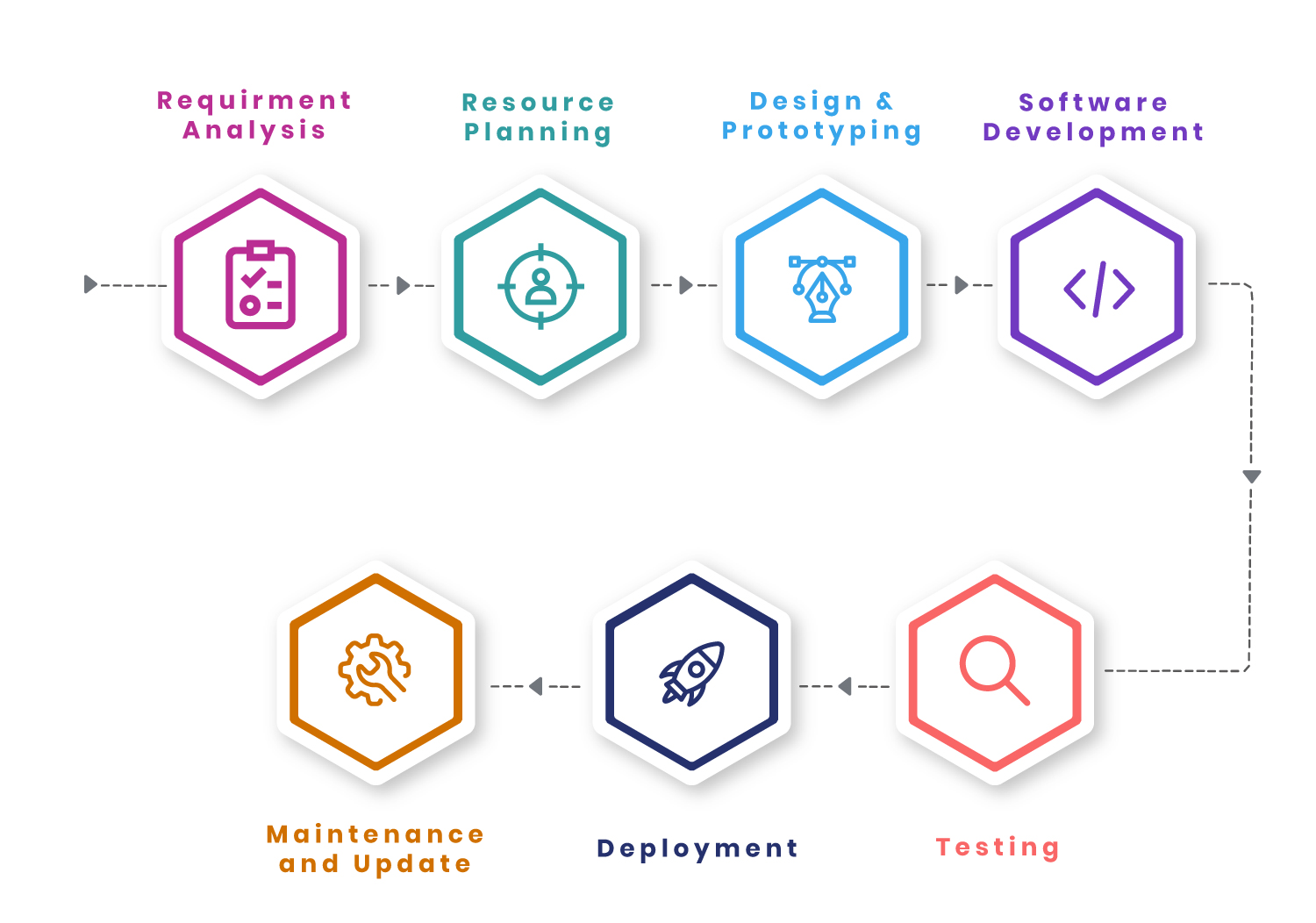
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) provided by Nichetech optimize the delivery of web content to users in the following ways:
- Global Network Infrastructure:
CDNs consist of a network of geographically distributed servers strategically placed in various locations worldwide. This network infrastructure reduces the physical distance between users and content, resulting in faster load times and improved performance.
- Content Caching and Distribution:
CDNs cache static and dynamic content, such as images, videos, scripts, and web pages, on edge servers located closer to end-users. When a user requests content, the CDN delivers it from the nearest edge server, reducing latency and minimizing the load on origin servers.
- Load Balancing:
CDNs balance incoming traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource utilization and ensure high availability and reliability. This helps mitigate the risk of server overload and downtime during peak traffic periods or sudden traffic spikes.
- Security Features:
CDNs offer security features such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection, SSL/TLS encryption, and Web Application Firewall (WAF) capabilities to safeguard websites and web applications from cyber threats and attacks.
- Content Optimization:
CDNs optimize content delivery by compressing files, resizing images, and leveraging HTTP/2 and other protocols to reduce file sizes and improve transfer speeds. This enhances the user experience and enables faster page loading times.
- Analytics and Monitoring:
CDNs provide insights into website performance, traffic patterns, and user behavior through analytics and monitoring tools. Businesses can use this data to optimize content delivery strategies, identify bottlenecks, and improve overall website performance.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
CDNs are designed to scale seamlessly to accommodate growing traffic volumes and changing user demands. SaaS-based CDNs offer flexible pricing models and scalable infrastructure resources, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on their needs and budget constraints.
In summary, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) provided by Nichetech optimize content delivery, improve website performance, and enhance the user experience by leveraging a distributed network infrastructure, caching technology, load balancing, security features, and content optimization techniques.
Cloudflare Enhances Cache Visibility and HTTP/3 Support for Faster Delivery
The landscape of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) continues to evolve rapidly, with new features and enhancements aimed at improving performance, security, and user experience.
Cloudflare:
-
Advanced Caching and Insights: Cloudflare has introduced granular visibility into cache performance, which includes detailed dashboards for monitoring and optimizing cache-hit ratios. This helps in identifying top URLs that miss the cache and improving overall site performance.
-
HTTP/3 Support: Cloudflare supports HTTP/3, utilizing QUIC for faster and more reliable connections.
Edgio Delivery:
-
Global Edge Network: Edgio Delivery focuses on secure and high-quality streaming with a robust network featuring over 300 Points of Presence (PoPs) and a capacity of 250+ Tbps. This ensures optimized content delivery and real-time analytics for better user experience.
-
Security Features: It includes advanced security measures like Origin Shield and Web Application Firewall (WAF) to protect against DDoS attacks.
Amazon CloudFront:
-
CloudFront Hosting Toolkit: Amazon has launched an open-source CLI tool to simplify the deployment of front-end applications in the cloud, enhancing both security and performance .
-
Integrated Monitoring: Amazon CloudFront now integrates with Amazon CloudWatch Internet Monitor, allowing for detailed insights into internet health and user experiences.
Fastly:
-
Real-time Control: Fastly offers real-time visibility and control over content caching and API settings, enabling swift modifications and rollbacks for improved agility.
-
Built-in Security: The CDN includes built-in DDoS protection, next-gen WAF, and TLS encryption, providing a secure environment for web and mobile applications.
Akamai:
-
Latency Reduction and Load Balancing: Akamai focuses on reducing latency and balancing loads to enhance the overall web experience. By distributing content closer to end-users, it minimizes buffering and ensures high availability even during traffic spikes.
-
Comprehensive Security: Akamai’s CDN offers robust security measures, including DDoS protection and cloud-based security solutions, to safeguard web infrastructure.
Content Delivery Made Easy: Simplify Your Online Presence with Nichetech's Expertise
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are the backbone of a fast and seamless online experience. But the world of CDNs is constantly evolving, offering new features and functionalities to meet the ever-growing demands of web content delivery. Here at Nichetech, we keep you informed about the latest updates in CDN Cloud Solutions:
Focus on Edge Computing and AI-powered Optimization:
-
Intelligent Edge Caching: CDNs are integrating with edge computing technologies to strategically cache content at network edges closer to users. This reduces latency and improves content delivery speeds, particularly for geographically diverse audiences.
-
AI-powered Content Caching and Optimization: CDNs are leveraging machine learning (ML) to analyze user behavior and network conditions. This allows them to dynamically cache content and optimize delivery based on real-time insights, further enhancing user experience.
-
Personalization at the Edge: CDNs are exploring ways to personalize content delivery at the edge using AI. This could involve tailoring content based on user location, device type, or browsing history, providing a more relevant and engaging user experience.
Security Enhancements and Threat Mitigation:
-
DDoS Mitigation with Advanced Techniques: CDNs are implementing new techniques to combat DDoS attacks, such as machine learning-based threat detection and automated mitigation strategies. This ensures high service availability and minimizes downtime during attacks.
-
Content Security and Bot Protection: CDNs are offering robust content security features to protect against web scraping, content theft, and malicious bot activity. This ensures the integrity and security of the content delivered through the CDN.
-
Integration with Cloud Security Solutions: CDNs are integrating with broader cloud security solutions to create a holistic security posture. This allows for centralized security management and better coordination between different security services.
Focus on Sustainability and Cost Optimization:
-
Green CDNs: There's a growing emphasis on green CDNs that utilize renewable energy sources to power their infrastructure and promote sustainable content delivery practices.
-
Cost-effective CDN Solutions: CDNs are offering flexible pricing models and features to cater to different business needs. This allows businesses to optimize CDN costs while maintaining high performance.
-
Automated CDN Optimization: CDNs are incorporating automation features to optimize resource allocation and content delivery based on real-time usage patterns. This reduces costs and ensures efficient resource utilization.
Nichetech assess your specific needs and demonstrate how CDN Cloud Solutions can empower you to deliver a faster, more secure, and engaging online experience for your audience. Let's navigate the evolving CDN landscape together and ensure your content reaches users globally with speed and efficiency!